How Does the Age of a VPS Server Affect Its Uptime and Downtime?
As businesses increasingly rely on the internet to conduct operations, the availability and reliability of their websites are critical. Virtual Private Servers (VPS) are a popular option for hosting websites due to their flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, the age of a VPS server can affect its uptime and downtime, which in turn can impact a website’s performance. In this article, we will explore the relationship between a VPS server’s age and its uptime and downtime.
Introduction to VPS Hosting
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a type of web hosting that allows businesses to host their websites on a virtual server that is partitioned from other websites on the same physical server. This partitioning creates a virtual environment that mimics a dedicated server, allowing businesses to customize their hosting environment and run their applications without interference from other websites.
Understanding Uptime and Downtime
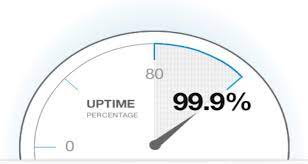
Uptime is the amount of time that a server is available and accessible to users. Downtime is the opposite of uptime, referring to the period when a server is not available or accessible to users. For businesses, downtime can result in lost revenue, decreased productivity, and damage to their reputation. Read more…
How VPS Age Affects Uptime and Downtime
The age of a VPS server can affect its uptime and downtime in several ways:
Hardware Failure
As the server ages, its hardware components are more likely to fail, leading to downtime. This can be due to factors such as wear and tear, heat damage, and power surges. Older servers may also have outdated hardware that is no longer supported by the manufacturer, making it difficult or impossible to replace failed components.
Software Updates
As technology evolves, software becomes more complex and resource-intensive. Newer servers are better equipped to handle the demands of modern software, whereas older servers may struggle to keep up. This can lead to downtime if software updates cause the server to crash or become unstable.
Security Vulnerabilities
Older servers may have security vulnerabilities that have been discovered and exploited by hackers. This can result in downtime if the server is compromised or taken offline for security updates. Newer servers are less likely to have these vulnerabilities and may have built-in security features that are not available on older servers.
Maintenance and Support
As the server ages, it may become more difficult to find replacement parts and support from the manufacturer. This can lead to longer downtime if repairs or maintenance are required. Newer servers are typically supported by the manufacturer for a longer period, making it easier to keep them running smoothly.
Best Practices for Maintaining VPS Uptime
To maintain high uptime for a VPS server, businesses should:
Regularly Monitor Server Performance
By monitoring server performance, businesses can detect potential issues before they become major problems. This can include monitoring CPU and memory usage, disk space, and network activity.
Keep Software Up to Date
To prevent security vulnerabilities and ensure compatibility with modern software, businesses should regularly update their VPS server’s software.
Replace Outdated Hardware
If a server’s hardware is outdated or prone to failure, businesses should consider replacing it with a newer server to maintain uptime.
Choose a Reliable Hosting Provider
Choosing a reliable hosting provider with a proven track record of high uptime can help businesses avoid downtime and ensure their website remains available to users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the age of a VPS server can have a significant impact on its uptime and downtime. Older servers are more likely to experience hardware failure, struggle with software updates, and have security vulnerabilities. By regularly monitoring server performance, keeping software up to date, replacing outdated hardware, and choosing a reliable hosting provider, businesses can maintain high
uptime for their VPS server and ensure their website remains accessible to users.
FAQs
-
Q: How long do VPS servers typically last? A: The lifespan of a VPS server depends on various factors such as the quality of the hardware, the level of maintenance, and the workload it handles. On average, a VPS server can last for 3-5 years before needing to be replaced.
-
Q: Can I improve the uptime of an older VPS server? A: Yes, regular maintenance, software updates, and hardware replacements can help improve the uptime of an older VPS server.
-
Q: What is the recommended uptime for a VPS server? A: The recommended uptime for a VPS server is 99.9% or higher.







